Why data pipeline development matters?
Data pipeline development refers to the data engineering service discipline that takes raw data from different sources and moves it into a destination – where it becomes reliable, on time, and ready for analysis. Pipelines take care of ingestion, cleansing, transformation, enrichment, validation, delivery, and of course getting the data ready for analysis, reporting, or writing to feature stores to be used in machine learning. When those pipeline features are absent, incomplete, or fragile, data will continue to become fragmented, stale, and unusable – stalling automation and elongated decision cycles.
The current market context elevates the importance of modern data platforms: the global big data and analytics market is expected to grow to USD 745 billion by 2030, as investment in the infrastructure that powers analytics and AI (Fortune Business Insights). Organizations that rely on data-driven decision making will need to master the analytics capacity of the data pipeline development.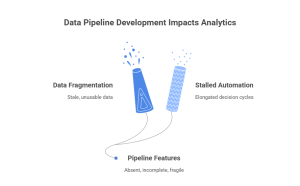
Core components of a production-ready pipeline
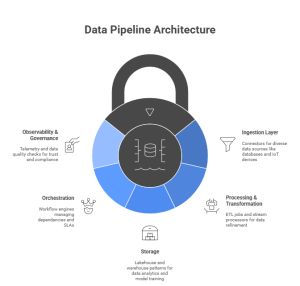
A production-grade pipeline architecture typically includes:
- Ingestion layer — batch and streaming connectors for databases, APIs, logs, IoT, and third-party feeds (e.g., Apache Kafka, AWS Kinesis).
- Processing & transformation — ETL/ELT jobs and stream processors such as Spark Structured Streaming or Flink; serverless functions for on-demand compute.
- Storage — lakehouse or warehouse patterns (Delta Lake, Snowflake) to support analytics and model training.
- Orchestration — workflow engines (Airflow, Prefect) that manage dependencies, retries, and SLAs.
- Observability & governance — telemetry, lineage, data quality checks, and policy enforcement to maintain trust and compliance
Designing clear interfaces between these layers simplifies testing, reduces operational risk, and enables independent scaling of components.
2025 trends shaping pipeline development
Real-time-first architectures
Real-time streaming advanced from being a “different from the standard” topic, to the new norm. Organizations now expect real-time or sub-second insights to deliver personalization, fraud detection, and real time operational control. Managed streaming services and significant advances in stream processing frameworks are reducing operational complexity and latency.
Lakehouse convergence
Lakehouse architectures combine the scale of data lakes with the transactional consistency of data warehouses. This pattern accommodates diverse workloads like analytical workloads and BI while reducing duplication and accelerating the time to insight.
Data observability and automated quality checks
Data observability is extremely important: telemetry, lineage, schema validation, and anomaly detection assist teams to understand and detect data pipeline drift with data quality regressions before their impact is felt by analysis consumers. If data observability is integrated at an early stage, incident mitigation times are reduced and confidence levels from stakeholders is increased.
Serverless and managed streaming
Serverless compute and managed streaming lower total cost of ownership and eliminate any capacity-planning burden. Management of elasticity and availability becomes the responsibility of the cloud provider and allows engineering teams to devote time to favoring business logic over capacity management.
AI-enabled pipeline automation
Pipeline automation is now even encroaching upon the design and runtime of pipelines: auto generated ETL/ELT code, schema evolution ‘assistants’, and intelligent retry/fallback patterns of activity allow engineers to be more productive with less manual effort.
Data mesh and domain ownership
A data mesh approach decentralizes data ownership by domain, enabling teams to ship data products independently while preserving centralized governance. This model helps organizations scale data delivery without creating bottlenecks.
Practical tools and patterns to consider
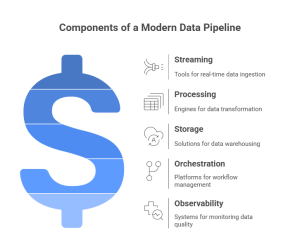
Choices depend on SLAs, data velocity, and workload profiles, but common components in 2025 architectures include:
- Streaming: Apache Kafka or managed Kafka (Confluent), AWS Kinesis.
- Processing: Spark Structured Streaming, Apache Flink, Databricks for unified stream/batch.
- Storage: Delta Lake, Snowflake, or a managed lakehouse.
- Orchestration: Apache Airflow, Prefect.
- Observability: integrated platforms that provide metrics, logs, lineage, and data quality alerts.
Business outcomes of well-engineered pipelines
Strong piping enables reliable results: acceleration to analytics, measures of model accuracy, reduced reconciliation, accountability by supporting operations. The results enable better predictions; improved inventory turns; responsive pricing; and better customer experiences.
In the real world of operating pipelines effectively, we see cross-functional teams working off a single source of truth where analysts build dashboards; data scientists build models using consistent feature sets; and operations teams act on near-real time information. Organizations that embrace platform based pipelines can often reduce multi-day reporting cycles to near-real-time insights with reduction in risk related to compliance and manual effort.
Techmango capability summary
Techmango delivers end-to-end data engineering services that align technical design with measurable business outcomes. Our practice covers ingestion and real-time streaming, lakehouse and warehouse design, ETL/ELT and transformation, data quality and observability, governance and compliance, MLOps enablement, and operational monitoring. We specialize in cloud-native deployments across AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, and deliver industry-focused solutions for logistics, e-commerce, finance, and global trade.
Final thoughts — practical guidance for 2025
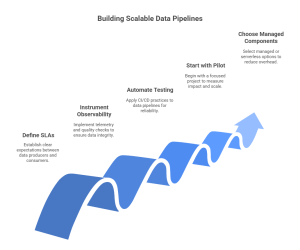
Mastering data pipeline development requires shifting from ad-hoc jobs toward platform thinking:
- Define SLAs and data contracts — make expectations explicit between producers and consumers.
- Instrument observability from day one — telemetry, lineage, and quality checks prevent downstream surprises.
- Automate testing and schema validation — treat data pipelines like software: CI/CD, unit tests, and rolling deployments.
- Start with a focused pilot — deliver a real-time dashboard, critical operational report, or ML feature store; measure impact, then scale.
- Choose managed or serverless components where they accelerate delivery — reduce operational overhead without sacrificing reliability.
At Techmango, our 450+ data engineering experts combine practical tooling choices, robust architecture patterns, and domain experience to implement resilient, scalable, and governed pipelines that turn raw data into reliable intelligence while reducing operational overhead.
Ready to accelerate your data journey? Contact Techmango to design and deploy production-ready pipelines that scale with your business.
Frequently Asked Questions
A data pipeline is a system that moves and transforms data from multiple sources into a destination where it’s reliable and ready for analysis. It’s essential for businesses to ensure accurate insights, faster decision-making, and automation without data fragmentation or delays.
A production-ready pipeline includes:
Ingestion: Connecting to databases, APIs, logs, IoT.
Processing & Transformation: ETL/ELT and stream processing.
Storage: Data warehouses or lakehouses.
Orchestration: Workflow management tools like Airflow.
Observability & Governance: Quality checks, telemetry, and lineage tracking.
Key trends include real-time streaming, lakehouse convergence, AI-assisted automation, serverless architectures, integrated observability, and data mesh for decentralized ownership and faster data delivery.
Well-engineered pipelines provide accurate and timely data, enabling faster analytics, better predictions, near real-time reporting, operational efficiency, and improved customer experiences while reducing manual effort and compliance risks.
Begin with a pilot project such as a real-time dashboard or ML feature store. Define SLAs and data contracts, implement observability from day one, automate testing and schema validation, and gradually scale using managed or serverless components to reduce operational overhead.

